Intel has added three new processors to its Xeon 6 CPU lineup, each designed with a specific goal in mind: to better support systems where GPUs drive the AI workload.
As demand for large-scale AI infrastructure continues to grow, the role of CPUs is shifting from being the main compute engine to managing, coordinating, and optimizing the broader system—especially in environments powered by high-end GPUs.

A Supporting Role in AI Infrastructure
The new chips include Performance-core (P-core) variants built for environments where CPUs are required to feed, control, and complement GPU operations. Intel’s emphasis in this update is not just on raw compute, but on how the CPU contributes to overall system efficiency.
One of the newly launched processors, the Xeon 6776P, is already being used in NVIDIA’s latest AI system, the DGX B300. In this context, the CPU’s job is less about performing AI model training itself, and more about managing data pipelines, orchestrating workloads, and maintaining consistent performance across all parts of the system.
Key Features: Priority Core Turbo and Turbo Frequency Control
Two features introduced in this round of Xeon chips stand out for their focus on workload-specific tuning:
-
Priority Core Turbo (PCT): This allows high-priority CPU cores to run at higher turbo frequencies, while less critical cores maintain lower speeds. This is especially useful for workloads where certain operations—like feeding data to GPUs—need to happen quickly and consistently.
-
Speed Select Technology – Turbo Frequency (SST-TF): This enables more fine-tuned control over how CPU frequencies are managed, letting systems allocate power and speed where they’re most needed in real time.
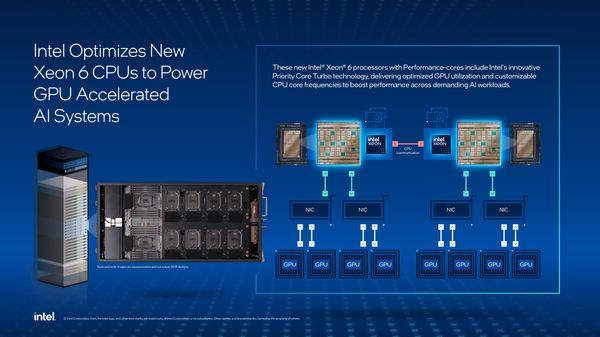
These kinds of features matter in environments where the CPU is constantly juggling data intake, memory transfers, and task distribution to GPUs.
Performance
Rather than trying to compete with GPUs on raw model training performance, these CPUs are built to optimize system-level throughput. Key specifications and features include:
-
Up to 128 Performance-cores per chip, giving them broad multitasking capacity.
-
30% improved memory speeds (compared to unnamed competitors), with support for high-capacity configurations using MRDIMMs and Compute Express Link (CXL).
-
Increased PCIe lane support, offering more bandwidth for data movement between components.
-
Support for FP16 arithmetic via Intel Advanced Matrix Extensions, useful for light AI operations like data preprocessing.
Intel also emphasizes reliability and serviceability, though these are standard expectations in the data center space.
Best Mobiles in India